Contents
Why Even Bother?
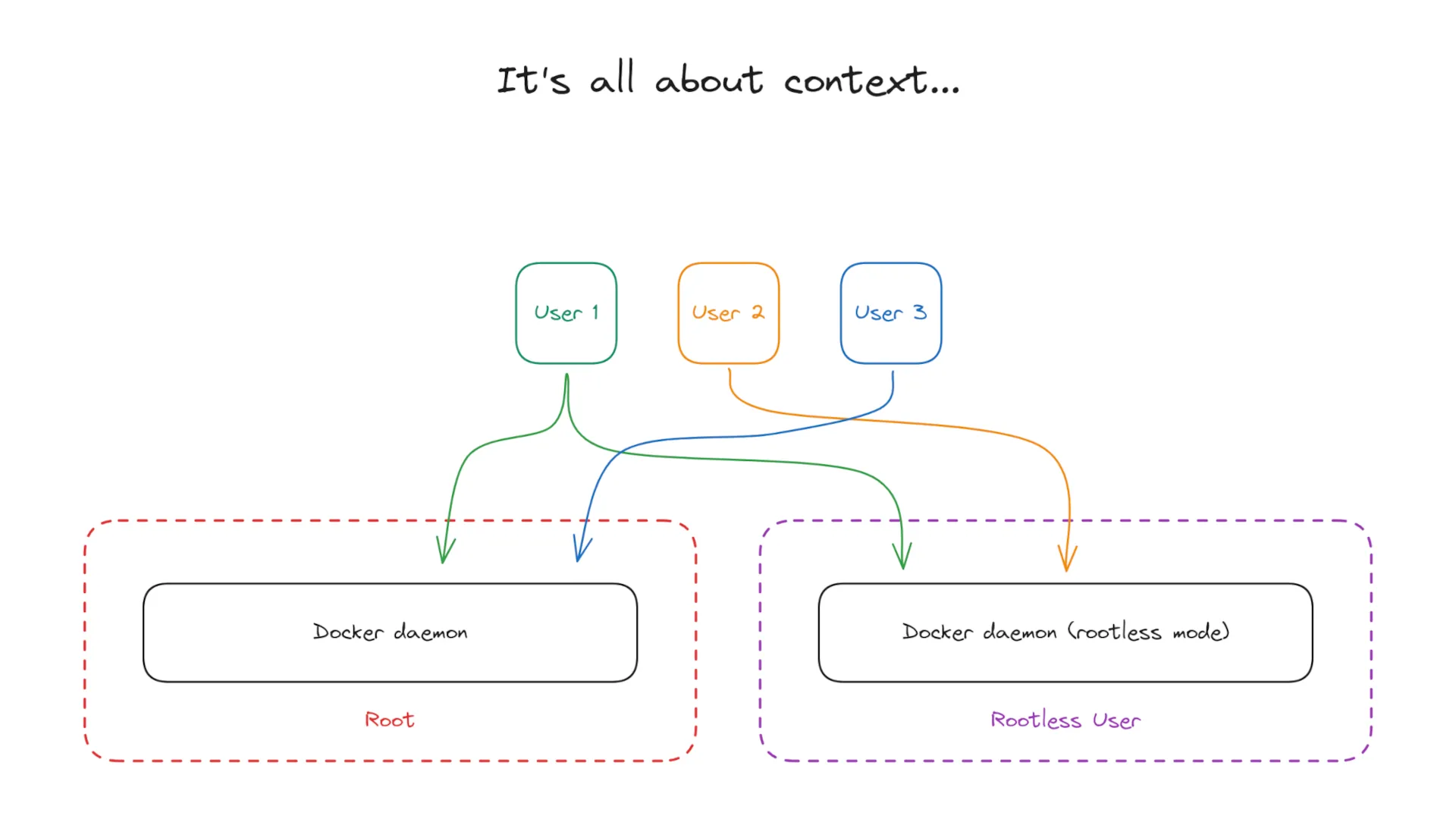
Even though it’s quite easy to install the Docker daemon in rootless mode, things can get hacky when you need this to work for more than one user.
Since I want my team to adopt it as the new default, and use privileged containers only when absolutely necessary, the solution must cause them as little friction as possible.
Useful for servers managed by a single person as well.
The Approach
- Install Docker, of course.
- Create a dedicated user for running rootless Docker.
- Install the rootless daemon.
Up until now, the points are obvious. What’s the catch?
If we leave it as it is, users will need to specify the ${DOCKER_HOST} explicitly, and run the cli as another user. Error-prone and inconvenient.
Damn, it would be nice to have something like kubeconfig contexts…
That’s where the special ingredient comes into play — Docker contexts. I feel like an idiot because the fact of their existence was unknown to me until like a week ago, when the thought above popped in my head 🫠.
Still, users don’t have access to the installed daemon’s socket. Empowering them to work freely in the dedicated user’s $HOME — where the socket is located by default — is kind of meh.
- Configure the daemon to use a separate location for its socket.
- Create a rootlesskit group for those who must be able to create and manage unprivileged containers.
- Set permissions on the socket and its directory to restrict access.
- Add a new context to users’ docker cli configs.
Configure
Prerequisites
The following needs to be installed first:
- Docker (including the docker-ce-rootless-extras package)
- systemd-container
- uidmap
- dbus-user-session
- acl
Info
The Daemon Itself
-
Create the user.
#
useradd -m cr -s $(which nologin) -
Create the group.
#
groupadd -U j_doe,e_alderson rootlesskitInfo
-
Enable lingering for the created user.
#
loginctl enable-linger cr -
Install the daemon.
#
machinectl shell cr@ /bin/bash -c 'dockerd-rootless-setuptool.sh install' -
Allow privileged ports (optional).
#
setcap cap_net_bind_service=ep $(which rootlesskit)Warning
-
Create a template for the directory to contain the socket.
#
cat << END > /usr/lib/tmpfiles.d/rootless.conf D /run/rootlesskit 1700 cr cr - - - a+ /run/rootlesskit - - - - g:rootlesskit:r-x,default:g:rootlesskit:rw- END☝️ This tells systemd to create a /run/rootlesskit directory at boot. Learn more here.
Since we don’t want anyone in the rootlesskit group to be able to delete the socket, a sticky bit is set on the directory.
The ACL on the line that starts with a+ ensures people can both read and write inside of the directory, but can’t delete it.
-
Override the daemon service to change the socket path.
-
Open the override file for editing.
#
machinectl shell cr@ /bin/bash -c 'systemctl --user edit docker' -
Add the following 👇.
# ExecStart is specified twice to reset the previous value first. [Service] ExecStart= ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd-rootless.sh -H unix:///run/rootlesskit/docker.socket
-
-
Reboot the server for changes to take effect.
$
systemctl reboot
Docker Context
Now, for each user in the rootlesskit group, add a new context.
$
docker context create rootless --docker host=unix:///run/rootlesskit/docker.socketAutomation
I’ve recently started developing an Ansible collection for Linux that contains a role for automating this setup.
As of now, it’s raw, undocumented, and supports only Ubuntu, but things will get better over time.
The repository will be publicly available as soon as I add at least some documentation. Stay tuned!
Developing a more or less general purpose collection that can be universally used by anyone turned out to be a tedious task, especially considering how much is going on in my life, and at work.
It’s sometimes not the most optimal solution even in terms of in-house projects. Most likely, we’ll just build pre-configured VM templates of various flavors: docker, rootless docker, no docker, etc.
Note on Systemd Resource Control
The Problem
In case you need to limit resource usage per container, it’s useful to know that on some systems manual configuration is needed for non-root users.
I was stuck on this problem while testing my website deployment on an Ubuntu VM. By default, delegated controllers for CPU management are not created.
The error may look like this:
NanoCPUs can not be set, as your kernel does not support CPU cfs period/quota or the cgroup is not mountedHow to Solve
Create an override for the user@ systemd service, and specify resources to create delegated controllers for.
Generally, it’s sufficient to logout and log back in after applying the override. For long-running background processes, a reboot is simpler.
Learn more on systemd resource control here.
Manually
-
Open the user@ service override file.
#
systemctl edit [email protected] -
👇 Add the following.
[Service] Delegate=memory pids cpu cpuset
Using Ansible
- name: Enable Systemd Resource Control Delegation
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Ensure systemd User Service Override Dir Present
become: true
ansible.builtin.file:
state: directory
path: /etc/systemd/system/[email protected]/
mode: '0755'
- name: Delegate Resource Management
become: true
register: delegate_override
ansible.builtin.copy:
content: |
[Service]
Delegate=memory pids cpu cpuset
dest: /etc/systemd/system/[email protected]/override.conf
mode: '0644'
- name: Restart Server
become: true
when: delegate_override.changed
ansible.builtin.reboot:The Result
As the result, what we have now is a convenient way of managing privileged and non-privileged containers using Docker.
The solution is scalable as well, since to allow new users to manage unprivileged containers on a server, they just need to be added to a group, and create a context 🎉.
vagrant@ubuntu-jammy:~$ docker context use rootless
rootless
Current context is now "rootless"
vagrant@ubuntu-jammy:~$ docker context ls
NAME DESCRIPTION DOCKER ENDPOINT ERROR
default Current DOCKER_HOST based configuration unix:///var/run/docker.sock
rootless * unix:///run/rootlesskit/docker.socket
vagrant@ubuntu-jammy:~$ docker compose ls
NAME STATUS CONFIG FILES
observability running(3) /var/lib/compose_projects/observability/compose.yml
vagrant@ubuntu-jammy:~$ docker --context default compose ls
NAME STATUS CONFIG FILES
httpd running(1) /var/lib/compose_projects/httpd/compose.yml
vagrant@ubuntu-jammy:~$